Jump to preprints or selected publications.
Preprints
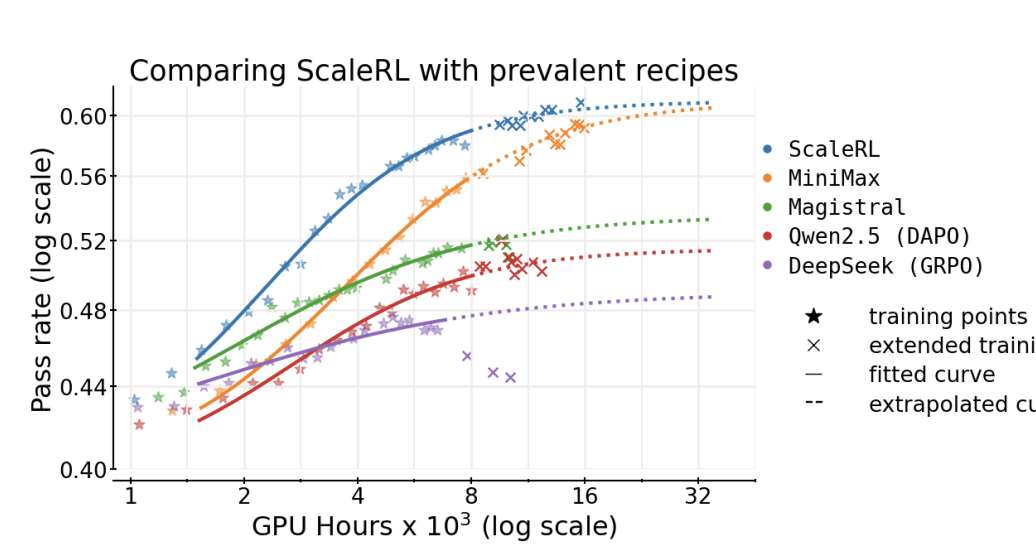
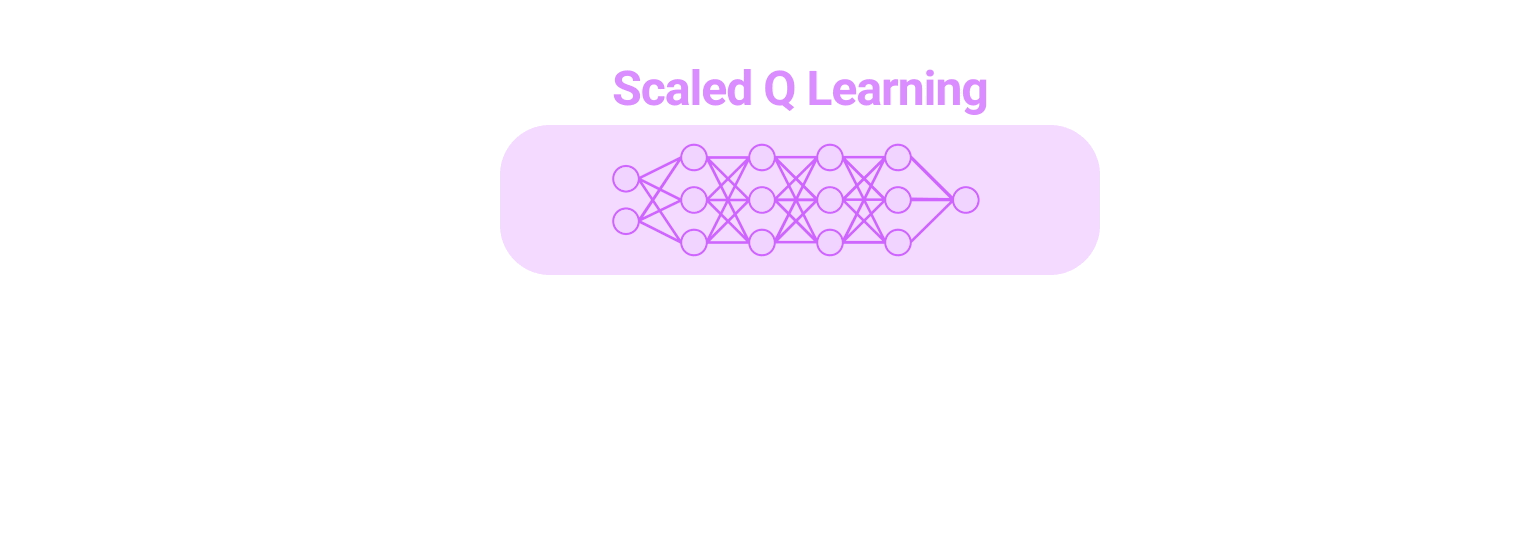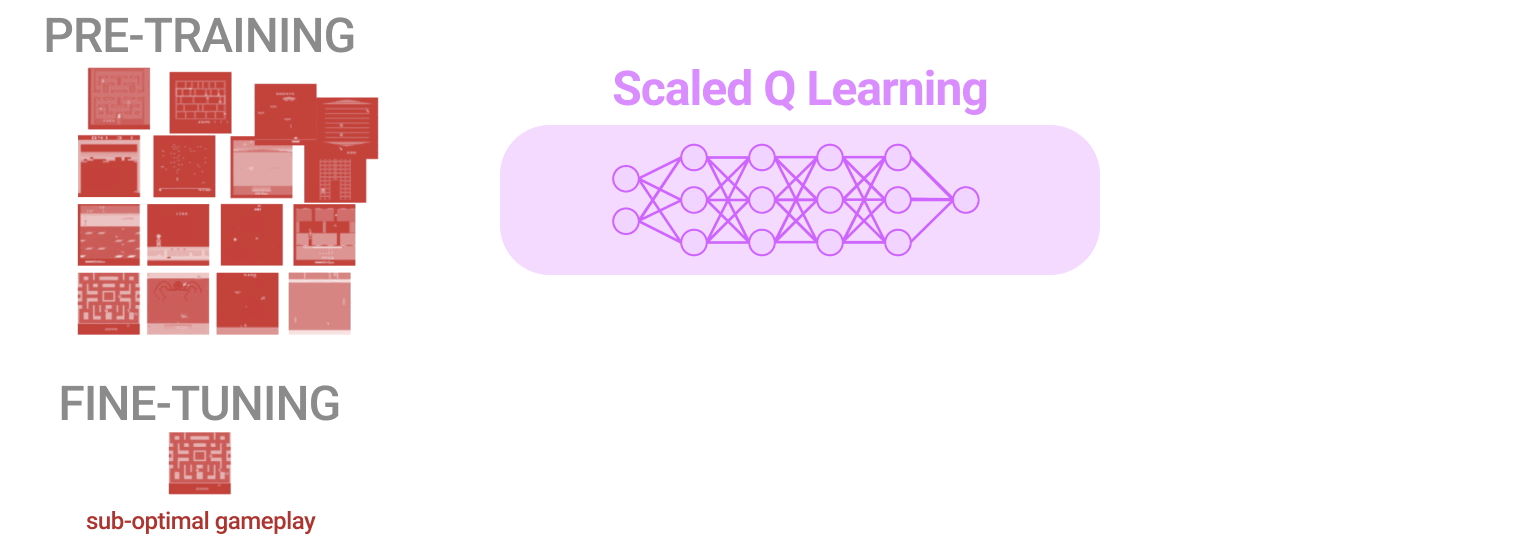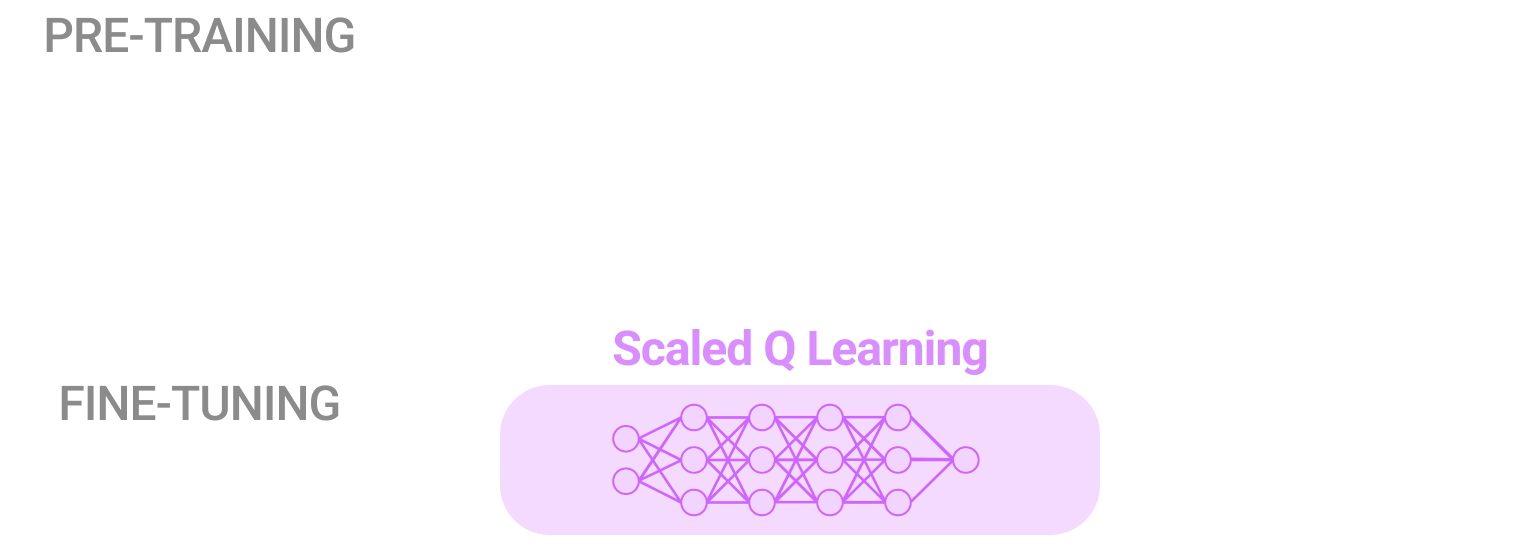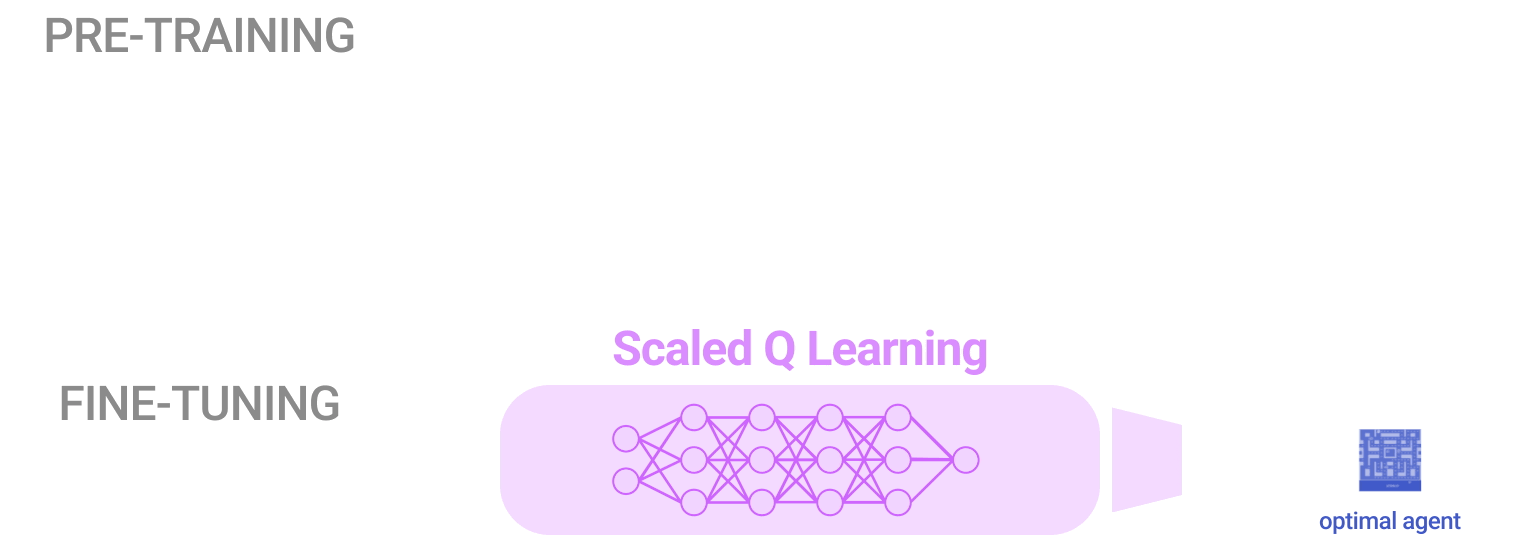
The Art of Scaling Reinforcement Learning Compute for LLMs
Devvrit Khatri, Lovish Madaan, ..., David Brandfonbrener, Rishabh Agarwal
This work provides both a framework to understand RL scaling and a practical recipe to make RL training as predictable as pre-training. RL scaling experiments costing 400K GB200 GPU hours, with a single 100K GPU hour run with predictable scaling.
Selected Publications
Generative Verifiers: Reward Modeling as Next-Token Prediction
Lunjun Zhang, Arian Hosseini, Hritik Bansal, Mehran Kazemi, Aviral Kumar, Rishabh Agarwal
ICLR 2025
Training generative reward models (GenRM) using next-token prediction, jointly on verification and solution generation. Such generative verifiers can use chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning,
and additional test-time compute via majority voting for better verification. Generative CoT verifiers trained on GSM generalizes to much harder problems in MATH!
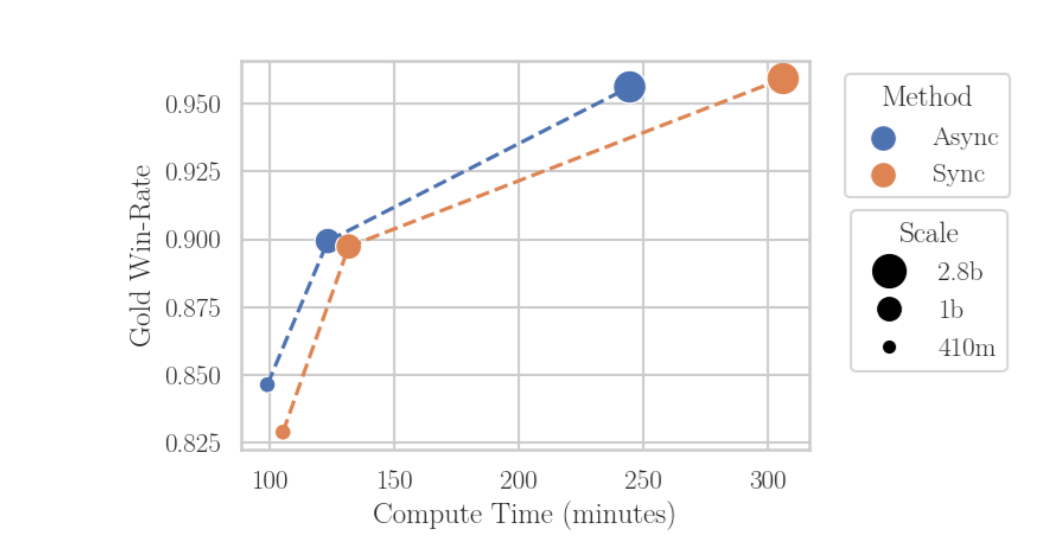
Asynchronous RLHF: Faster and More Efficient Off-Policy RL for Language Models
Michael Noukhovitch, Shengyi Huang, ..., Rishabh Agarwal, Aaron Courville
ICLR 2025
Inspired by classical deep RL, we propose separating generation and learning in RLxF.
This enables asynchronous generation of new samples while simultaneously training on old samples, leading to faster training and more compute-optimal scaling.
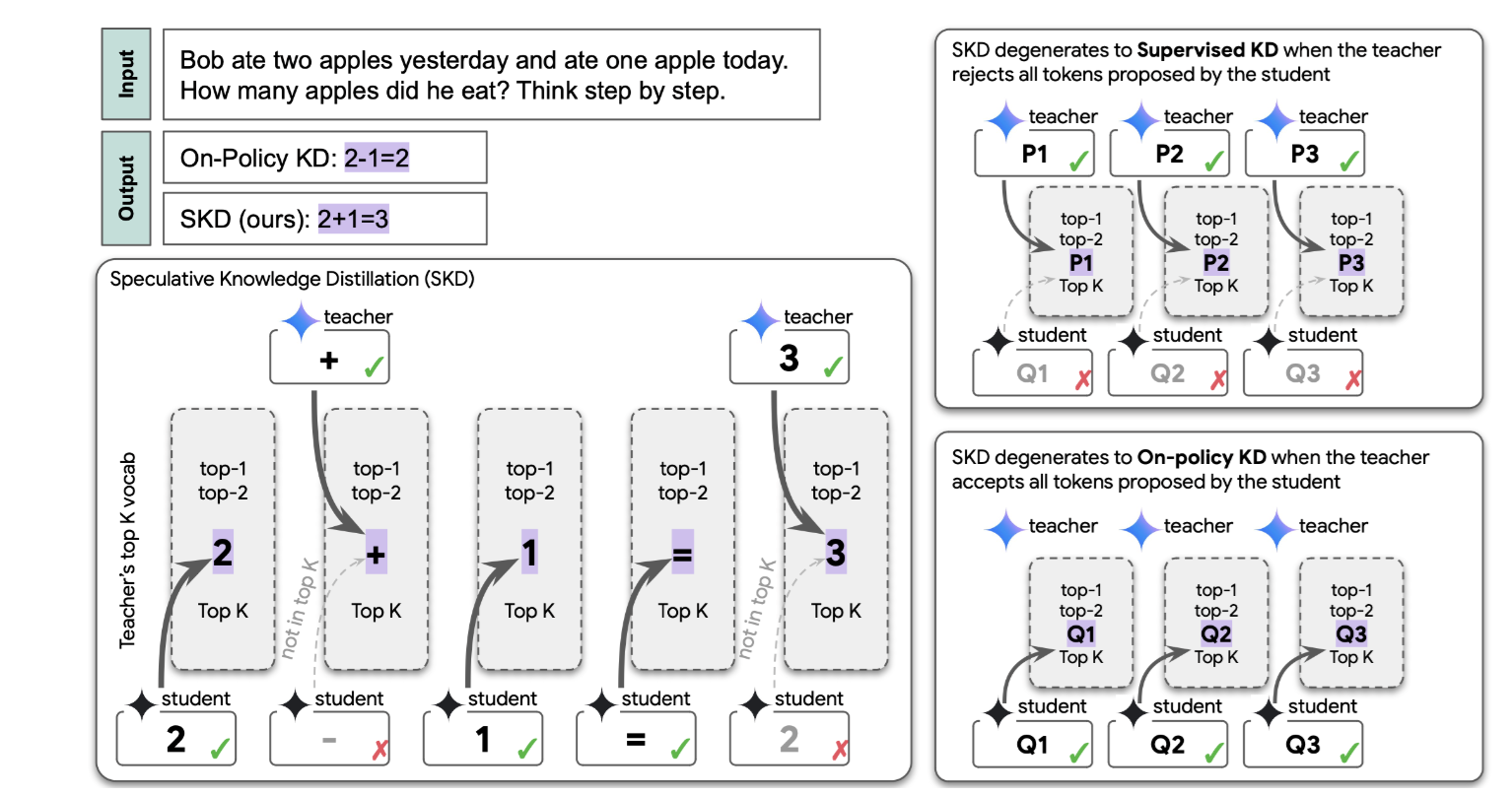
Speculative Knowledge Distillation: Bridging the Teacher-Student Gap Through Interleaved Sampling
Wenda Xu, ..., Rishabh Agarawl^, Chen-Yu Lee^, Tomas Pfister
ICLR 2025
An improvement to on-policy distillation where the student proposes tokens, but the teacher replaces tokens outside its top-k tokens to avoid low quality samples.
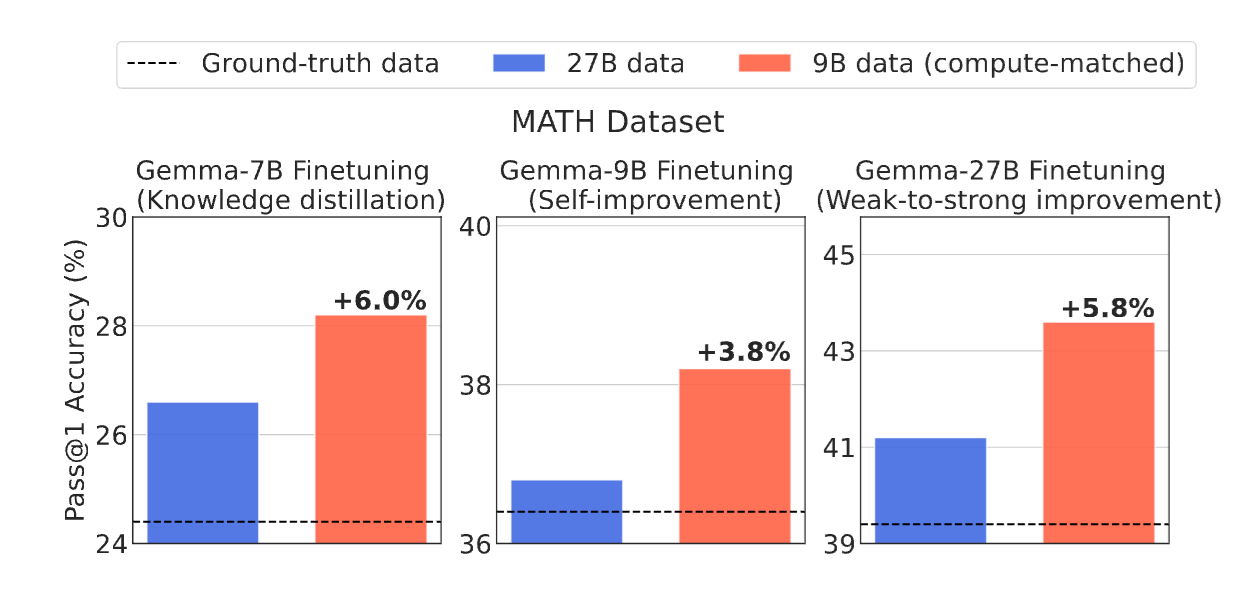
Smaller, Weaker, Yet Better: Training LLM Reasoners via Compute-Optimal Sampling
Hritik Bansal, Arian Hosseini, Rishabh Agarwal, Vinh Tran, and Mehran Kazemi
ICLR 2025
Under a fixed inference compute or cost budget, fine-tuning on data generated from a smaller but weaker LLM outperform those trained on stronger but larger models.
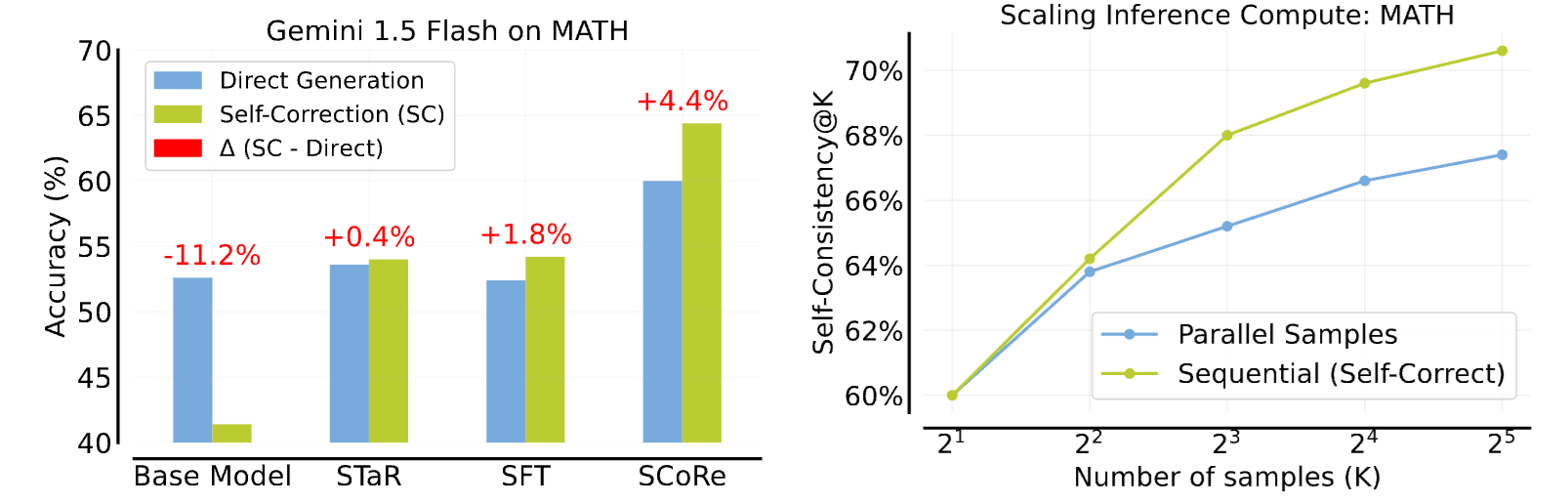
Training Language Models to Self-Correct via Reinforcement Learning
A Kumar*, V Zhuang*, Rishabh Agarwal*, Y Su* et al.
ICLR 2025 (Oral)
A multi-turn online RL approach that teaches an LLM to self-correct using entirely self-generated data.
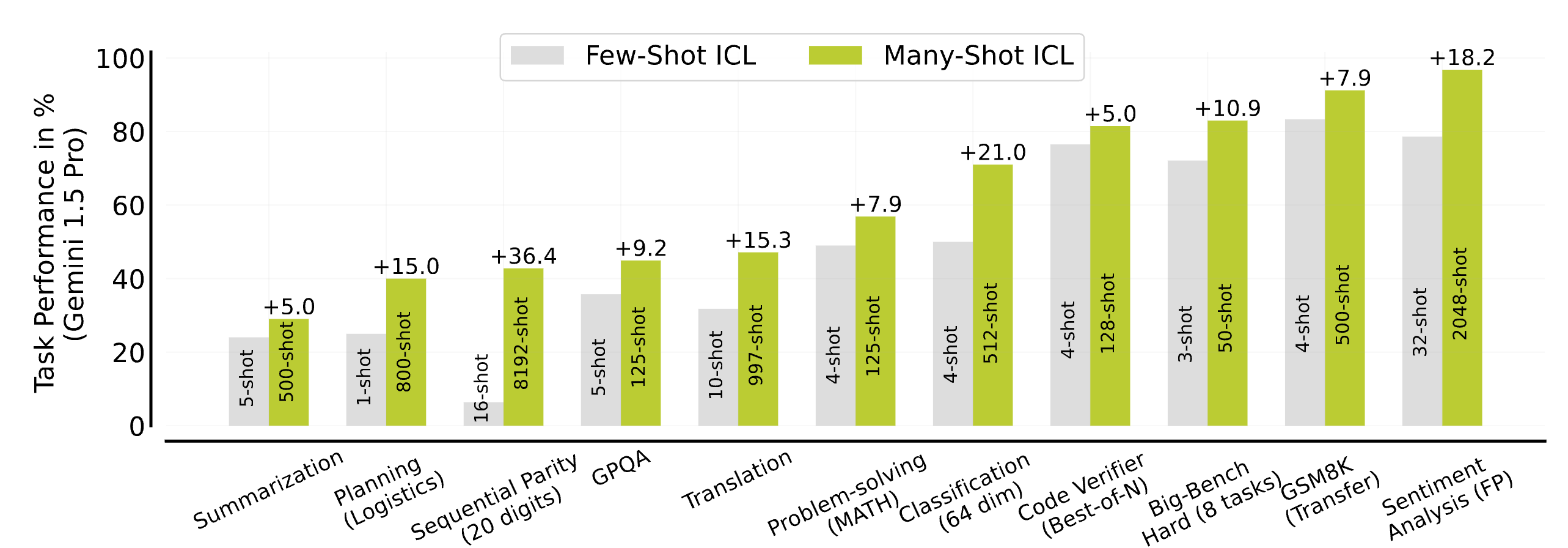
Many-Shot In-Context Learning
Rishabh Agarwal*, Avi Singh*, Lei M. Zhang, Bernd Bohnet, Luis Rosias, Stephanie Chan et al.
NeurIPS 2024 (Spotlight), Oral@ICML Long-Context Workshop
Explores ICL with hundreds or thousands of examples. Unlike few-shot learning, many-shot learning is
effective at overriding pretraining biases, can learn high-dimensional functions with numerical inputs, and performs comparably to fine-tuning.
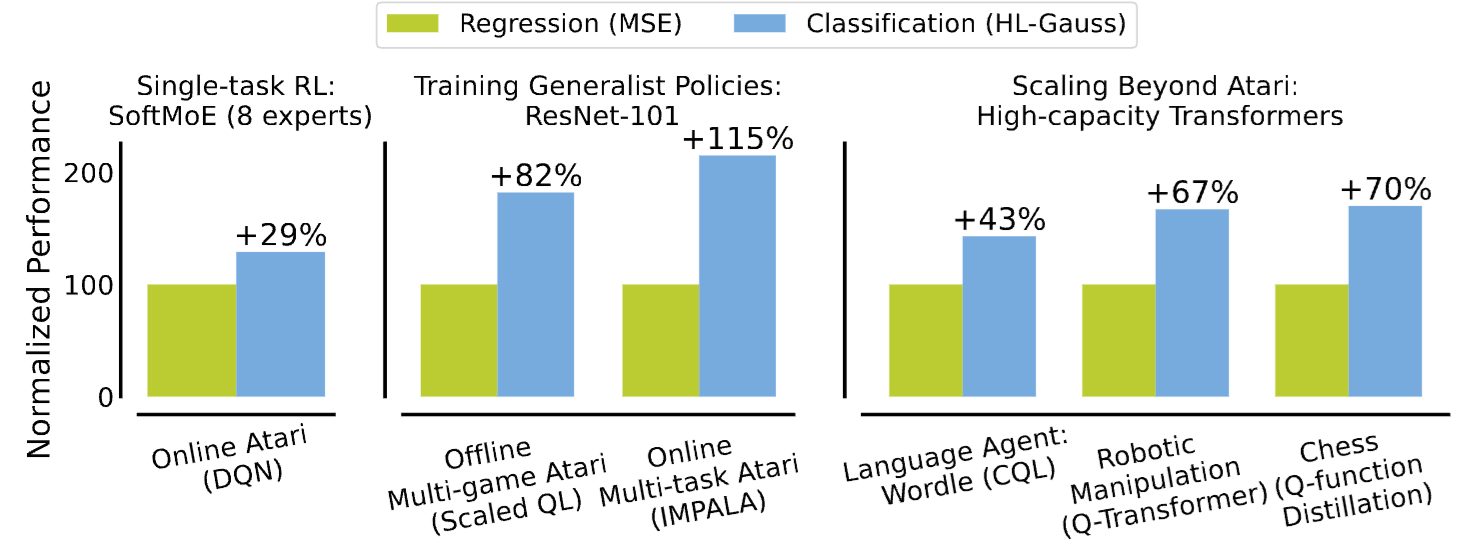
Stop Regressing: Training Value Functions via Classification for Scalable Deep RL
Jesse Farebrother*, Jordi Orbay, ..., Pablo Castro, Aviral Kumar, Rishabh Agarwal*
ICML 2024 (Oral)
Training value functions with categorical cross-entropy can substantially improve the scalability and generalizability of deep RL at little-to-no cost.
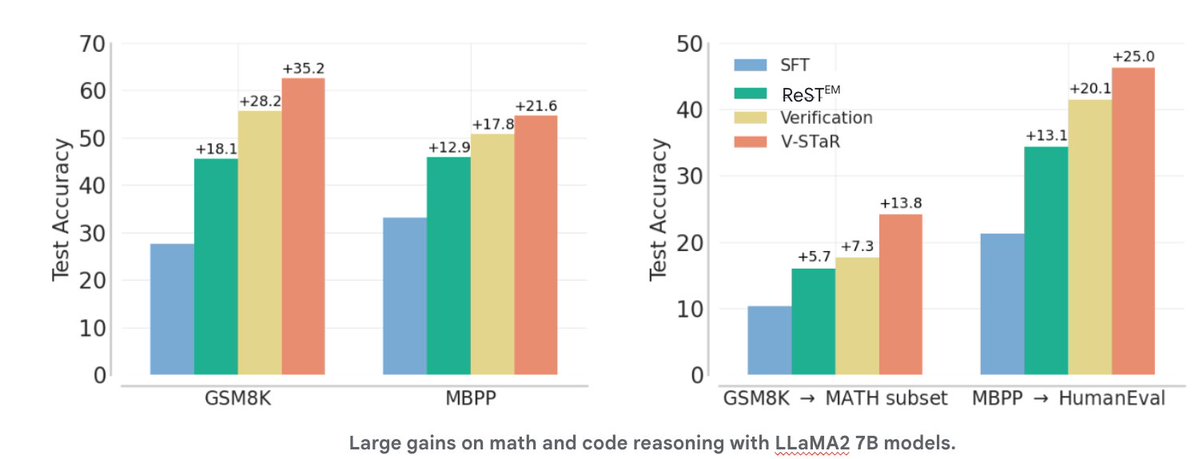
V-STaR: Training Verifiers for Self-Taught Reasoners
Arian Hosseini, Xingdi Yuan, Nikolay Malkin, Aaron Courville, Alessandro Sordoni, Rishabh Agarwal
CoLM 2024
Self-improvement approaches, such as ReST^EM and STaR, discard all the LLM-generated incorrect solutions during training. V-STaR
augments such approaches by training a verifier using both correct and incorrect solutions, used at test-time for re-ranking LLM generations.
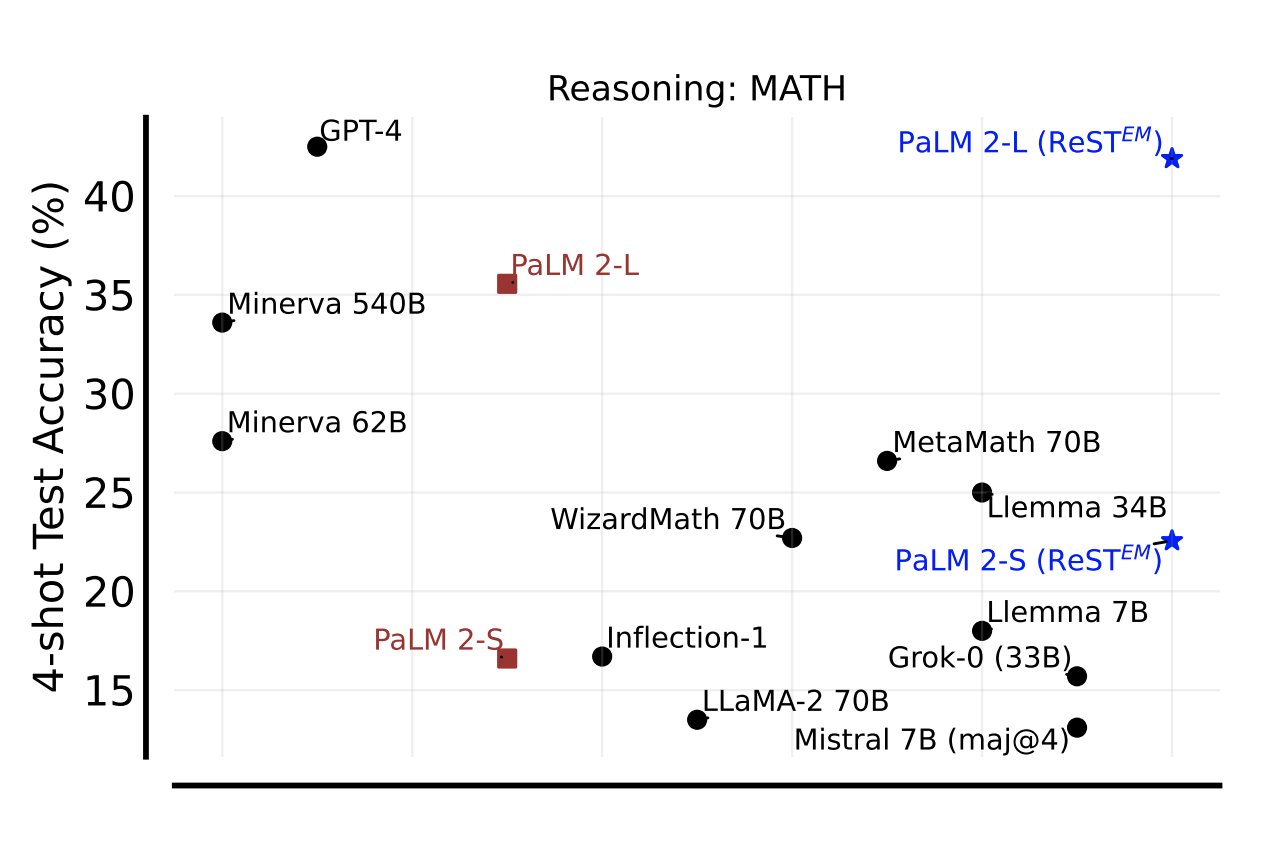
Beyond Human Data: Scaling Self-Training for Problem-Solving with Language Models
Avi Singh*, JD Coreyes*, Rishabh Agarwal* et al.
TMLR 2024
We explore whether we can go beyond human data on tasks where we have access to scalar feedback, finding that
a simple self-training method based on expectation-maximization can substantially reduce dependence on human-generated data.
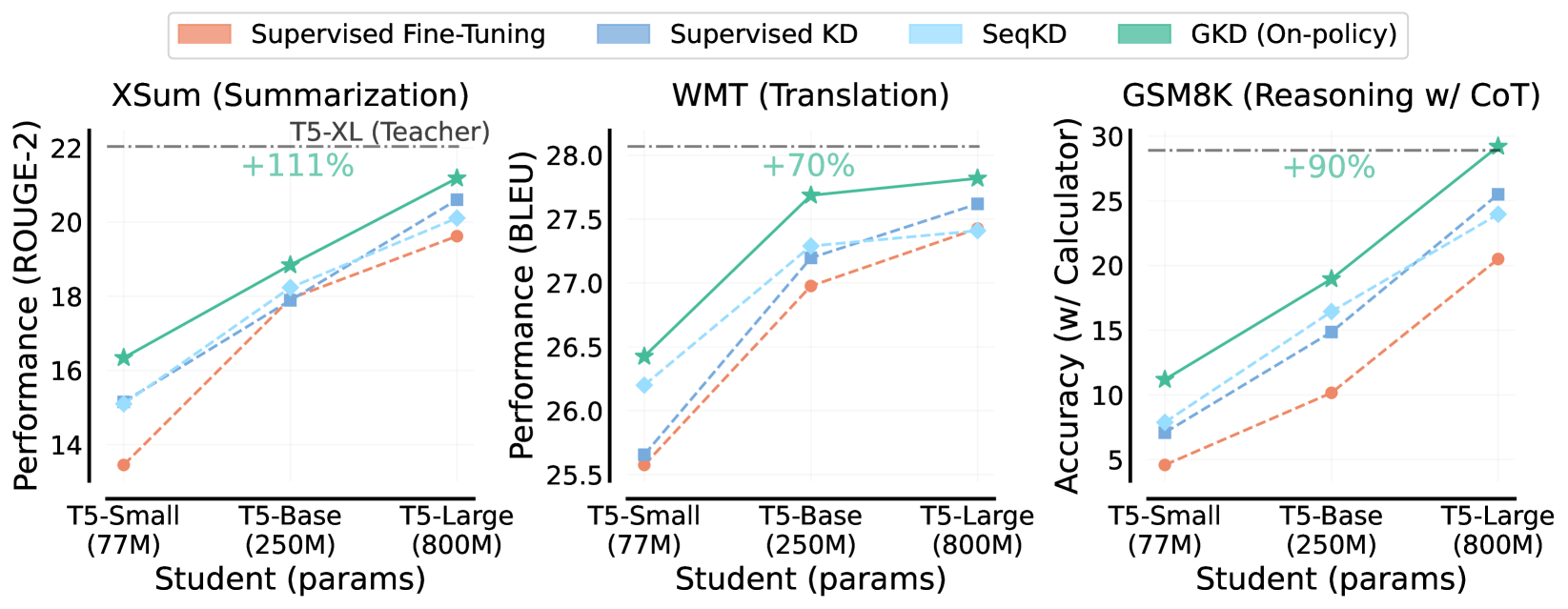
On-Policy Distillation of Language Models: Learning from Self-Generated Mistakes
Rishabh Agarwal*, Nino Vieillard*, Piotr Stanczyk, Sabela Ramos, Matthieu Geist, Olivier Bachem
ICLR 2024
GKD tackles distribution-mismatch in distilling autoregressive models, and outperforms commonly-used approaches on distilling LLMs for
summarization, translation and reasoning tasks. Used for post-training distillation for Gemma 2,Gemma 3, and Qwen-3 Thinking .
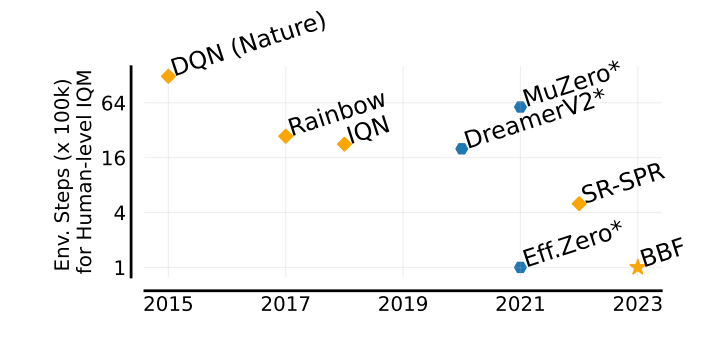
Bigger, Better, Faster: Human-level Atari with human-level efficiency
Max Schwarzer, Johan Obando-Ceron, Aaron Courville, Marc Bellemare, Pablo Samuel Castro*, Rishabh Agarwal*
ICML 2023
With scaling compute and model size along with appropriate design choices, value-based methods achieve super-human performance in the Atari 100K, while being 4x compute efficient than SOTA.
Offline Q-Learning on Diverse Multi-Task Data Both Scales And Generalizes
Aviral Kumar, Rishabh Agarwal, Xinyang Geng, George Tucker, Sergey Levine
ICLR 2023 (Top 5%), NeurIPS 2022 DRL Workshop Best paper Runner-up
With appropriate design choices, offline Q-learning exhibit strong performance that scales with model capacity. The secret ingredients
were training on a large and diverse offline dataset with ResNets, distributional C51 backups and feature normalization (that is make RL training look more like SL).
Beyond Tabula Rasa: Reincarnating Reinforcement Learning
Rishabh Agarwal, Max Schwarzer, Pablo Samuel Castro, Aaron Courville, Marc G. Bellemare
NeurIPS 2022
This work proposes an alternative research workflow to tabula rasa RL, where prior computational work (e.g., learned policies) is transferred from agent to another.
Deep RL at the Edge of the Statistical Precipice
Rishabh Agarwal, Max Schwarzer, Pablo Samuel Castro, Aaron Courville, Marc G. Bellemare
NeurIPS 2021 (Outstanding Paper Award)
Our findings call for a change in how we evaluate performance on deep RL benchmarks, for which we present more reliable protocols and an
open-source library , easily applicable with *even a handful of runs*, to prevent unreliable results
from stagnating the field.
Contrastive Behavioral Similarity Embeddings for Generalization in Reinforcement Learning
Rishabh Agarwal, Marlos C. Machado, Pablo Samuel Castro, Marc G. Bellemare
ICLR 2021 (Spotlight)
To improve generalization, we learn representations, via a contrastive loss, that puts states together with similar long-term optimal behavior. This is orthogonal to existing
approaches such as data augmentation. An earlier version was accepted as an oral presentation at NeurIPS 2020 Workshop on Biological and Artificial RL.
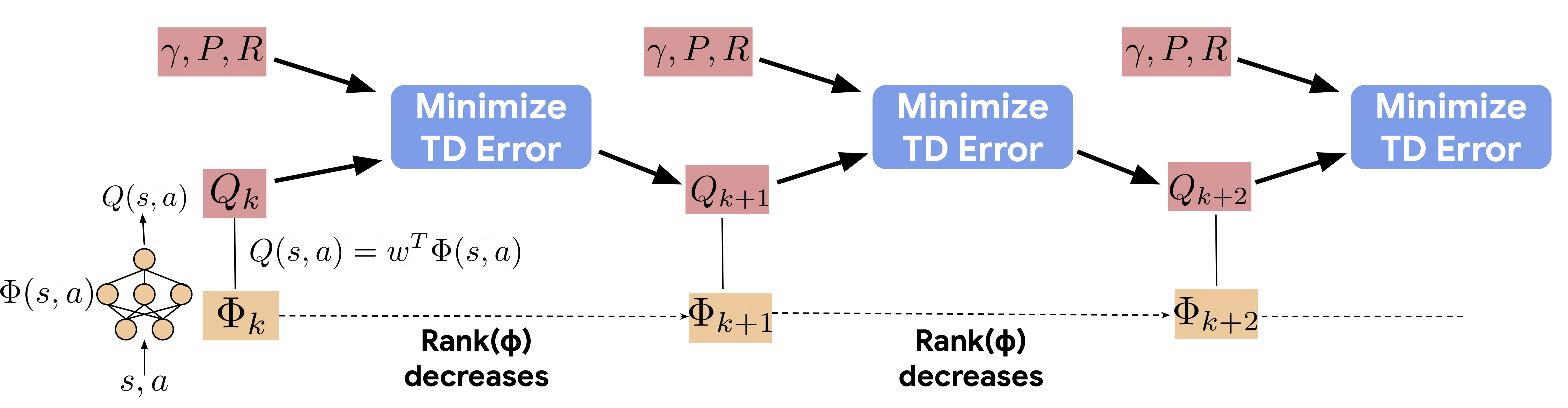
Implicit Under-Parameterization Inhibits Data-Efficient Deep Reinforcement Learning
Aviral Kumar*, Rishabh Agarwal*, Dibya Ghosh, Sergey Levine
ICLR 2021
We identify an implicit under-parameterization phenomenon in value-based deep RL methods that use bootstrapping: when value functions,
approximated using deep neural networks, are trained with gradient descent using iterated regression onto target values generated by
previous instances of the value network, more gradient updates decrease the expressivity of the current value network.
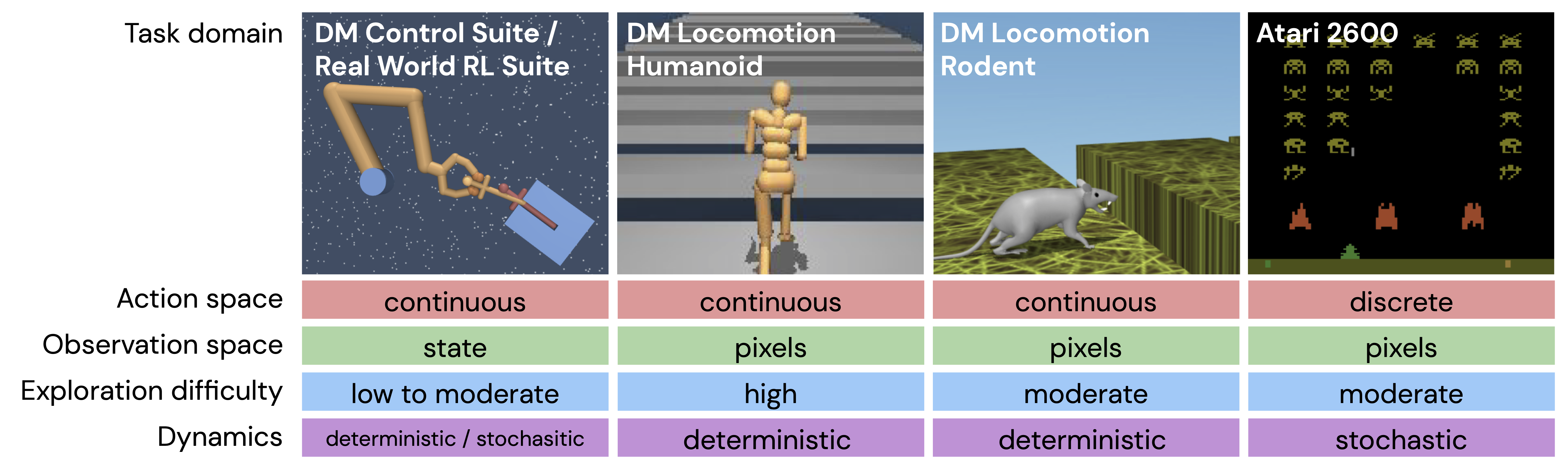
RL Unplugged: Benchmarks for Offline Reinforcement Learning
Caglar Gulcehre, Ziyu Wang, Alexander Novikov, Tom Le Paine, Sergio Gómez Colmenarejo, Konrad Zolna, Rishabh Agarwal,
Josh Merel, Daniel Mankowitz, Cosmin Paduraru, Gabriel Dulac-Arnold, Jerry Li, Mohammad Norouzi, Matt Hoffman, Ofir Nachum,
George Tucker, Nicolas Heess, Nando de Freitas
NeurIPS 2020
We propose a benchmark called RL Unplugged to evaluate and compare offline RL methods on a diverse range of domains. We provide detailed evaluation
protocols for each domain and provide an extensive analysis of existing methods using these protocols. We hope that our suite of benchmarks will
increase the reproducibility in offline RL and make it possible to study challenging tasks with a limited computational budget, thus making RL research
both more systematic and more accessible across the community.
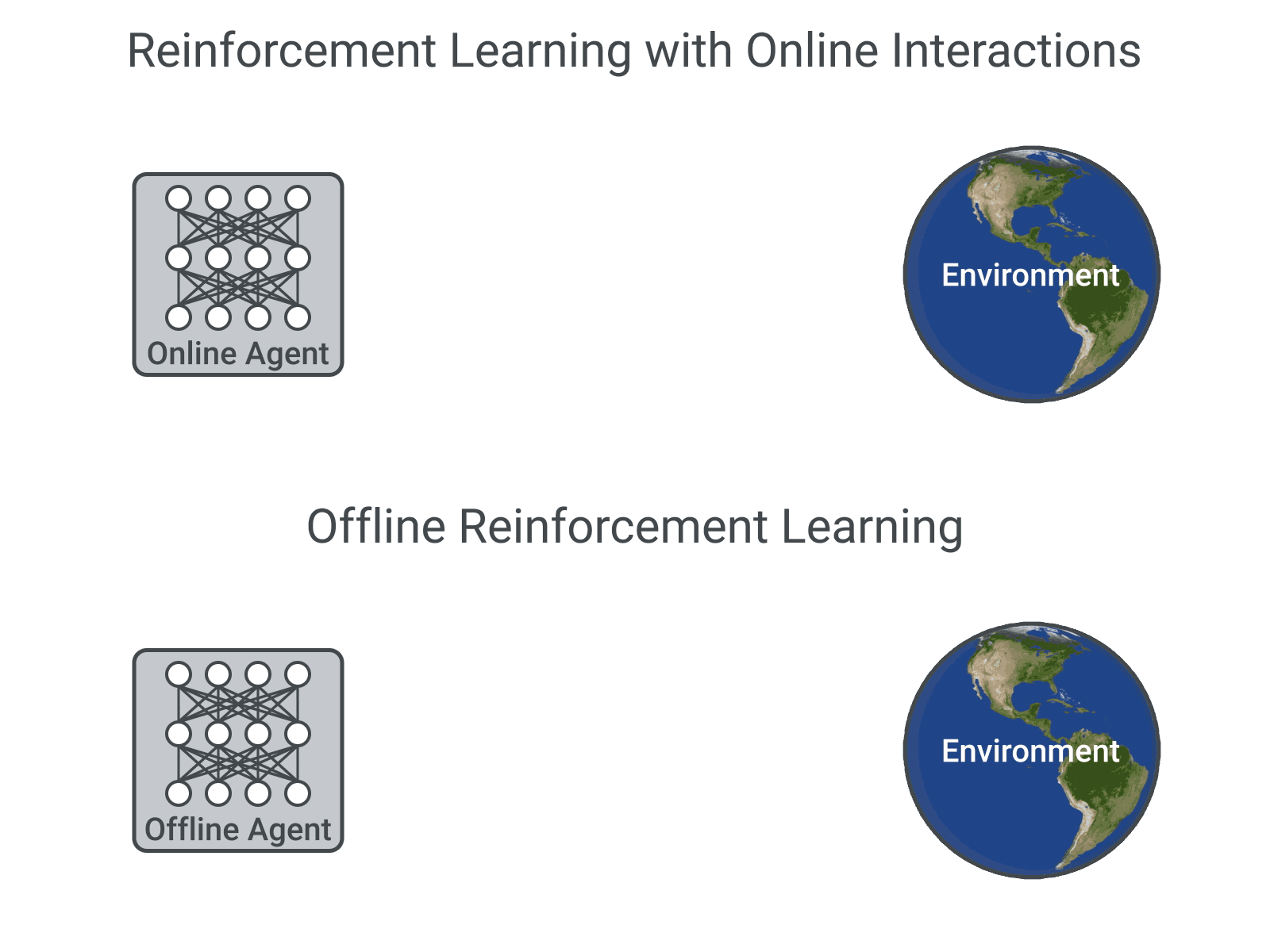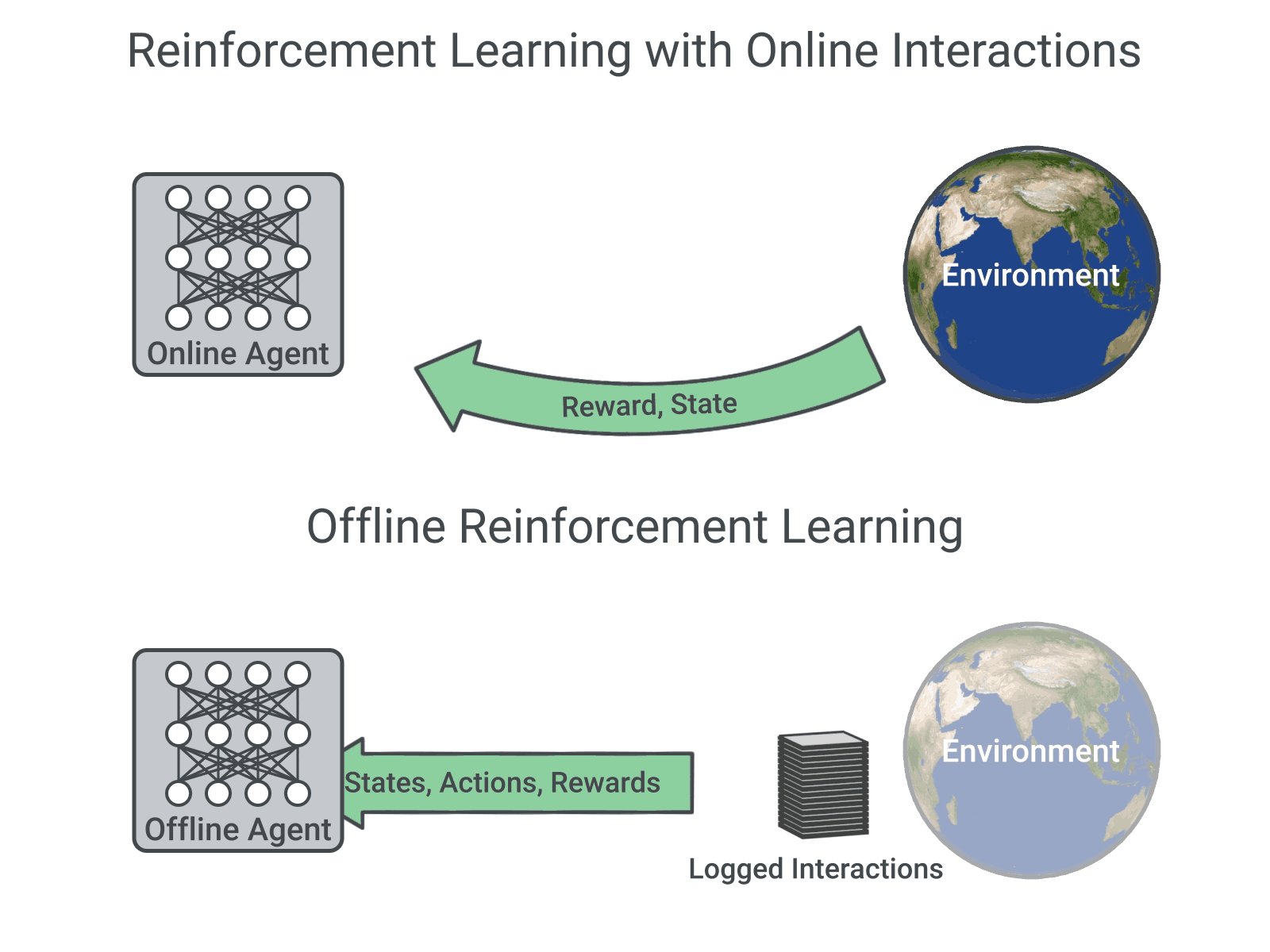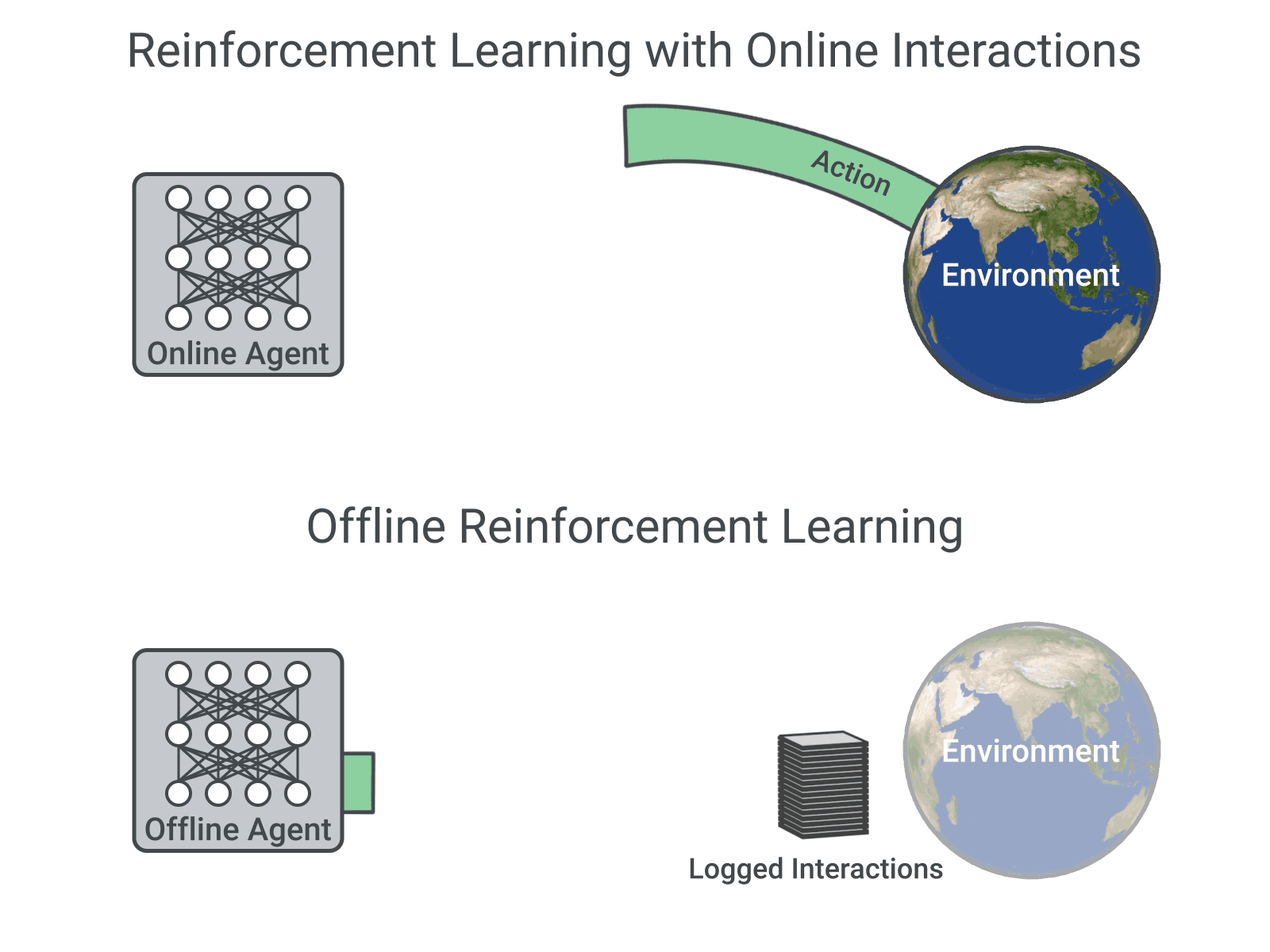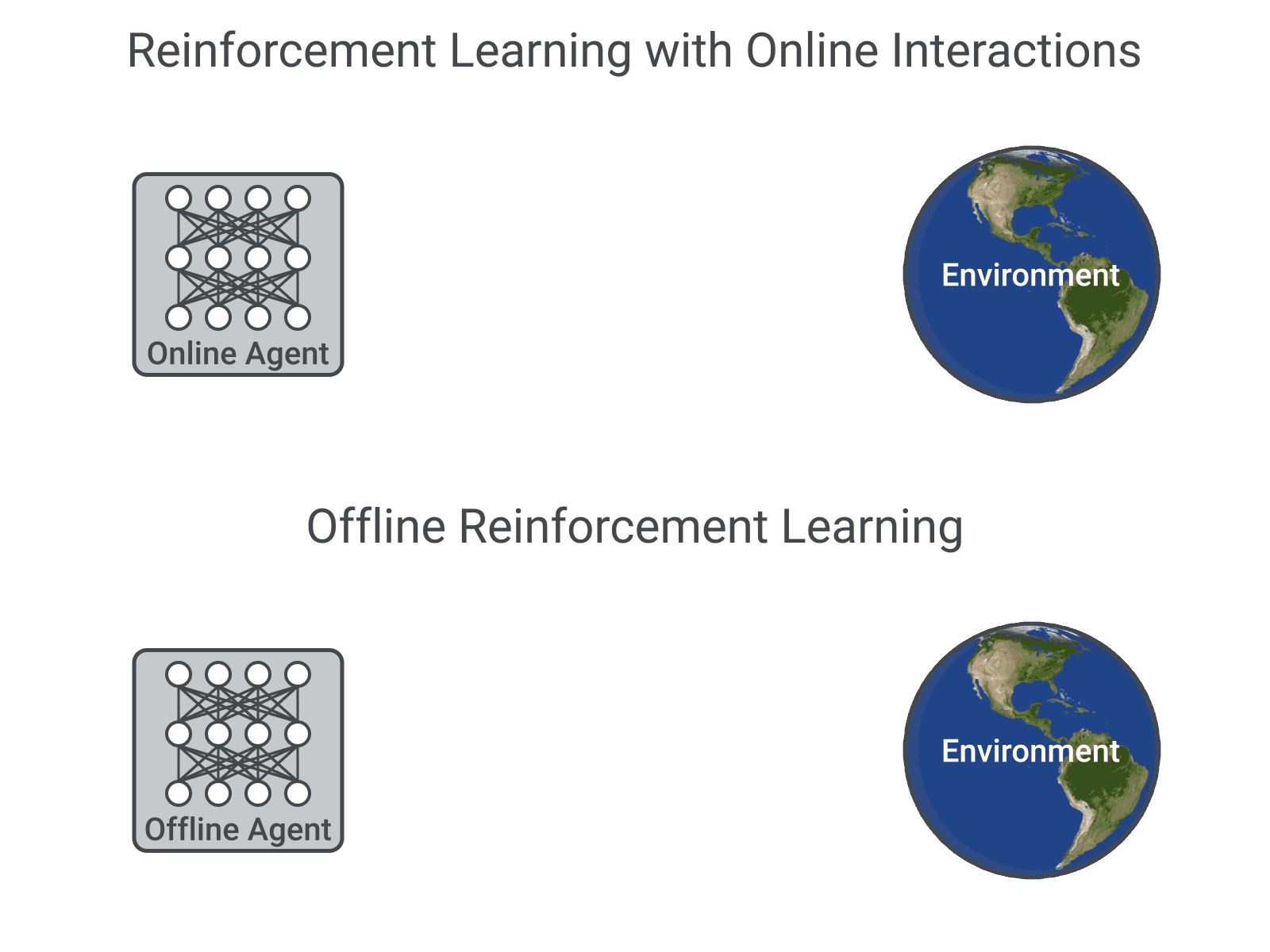
An Optimistic Perspective on Offline Reinforcement Learning
Rishabh Agarwal, Dale Schuurmans, Mohammad Norouzi
ICML 2020 (Talk)
This paper popularized offline RL and showed that standard off-policy algorithms perform quite well in the fully
off-policy / offline deep RL setting with large and diverse datasets. A previous version was titled "Striving for Simplicity in Off-Policy Deep Reinforcement Learning"
and presented as a contributed talk at NeurIPS 2019 DRL workshop.
Devvrit Khatri, Lovish Madaan, ..., David Brandfonbrener, Rishabh Agarwal
This work provides both a framework to understand RL scaling and a practical recipe to make RL training as predictable as pre-training. RL scaling experiments costing 400K GB200 GPU hours, with a single 100K GPU hour run with predictable scaling.
Lunjun Zhang, Arian Hosseini, Hritik Bansal, Mehran Kazemi, Aviral Kumar, Rishabh Agarwal
ICLR 2025
Training generative reward models (GenRM) using next-token prediction, jointly on verification and solution generation. Such generative verifiers can use chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning, and additional test-time compute via majority voting for better verification. Generative CoT verifiers trained on GSM generalizes to much harder problems in MATH!
Michael Noukhovitch, Shengyi Huang, ..., Rishabh Agarwal, Aaron Courville
ICLR 2025
Inspired by classical deep RL, we propose separating generation and learning in RLxF. This enables asynchronous generation of new samples while simultaneously training on old samples, leading to faster training and more compute-optimal scaling.
Wenda Xu, ..., Rishabh Agarawl^, Chen-Yu Lee^, Tomas Pfister
ICLR 2025
An improvement to on-policy distillation where the student proposes tokens, but the teacher replaces tokens outside its top-k tokens to avoid low quality samples.
Hritik Bansal, Arian Hosseini, Rishabh Agarwal, Vinh Tran, and Mehran Kazemi
ICLR 2025
Under a fixed inference compute or cost budget, fine-tuning on data generated from a smaller but weaker LLM outperform those trained on stronger but larger models.
A Kumar*, V Zhuang*, Rishabh Agarwal*, Y Su* et al.
ICLR 2025 (Oral)
A multi-turn online RL approach that teaches an LLM to self-correct using entirely self-generated data.
Rishabh Agarwal*, Avi Singh*, Lei M. Zhang, Bernd Bohnet, Luis Rosias, Stephanie Chan et al.
NeurIPS 2024 (Spotlight), Oral@ICML Long-Context Workshop
Explores ICL with hundreds or thousands of examples. Unlike few-shot learning, many-shot learning is effective at overriding pretraining biases, can learn high-dimensional functions with numerical inputs, and performs comparably to fine-tuning.
Jesse Farebrother*, Jordi Orbay, ..., Pablo Castro, Aviral Kumar, Rishabh Agarwal*
ICML 2024 (Oral)
Training value functions with categorical cross-entropy can substantially improve the scalability and generalizability of deep RL at little-to-no cost.
Arian Hosseini, Xingdi Yuan, Nikolay Malkin, Aaron Courville, Alessandro Sordoni, Rishabh Agarwal
CoLM 2024
Self-improvement approaches, such as ReST^EM and STaR, discard all the LLM-generated incorrect solutions during training. V-STaR augments such approaches by training a verifier using both correct and incorrect solutions, used at test-time for re-ranking LLM generations.
Avi Singh*, JD Coreyes*, Rishabh Agarwal* et al.
TMLR 2024
We explore whether we can go beyond human data on tasks where we have access to scalar feedback, finding that a simple self-training method based on expectation-maximization can substantially reduce dependence on human-generated data.
Rishabh Agarwal*, Nino Vieillard*, Piotr Stanczyk, Sabela Ramos, Matthieu Geist, Olivier Bachem
ICLR 2024
GKD tackles distribution-mismatch in distilling autoregressive models, and outperforms commonly-used approaches on distilling LLMs for summarization, translation and reasoning tasks. Used for post-training distillation for Gemma 2,Gemma 3, and Qwen-3 Thinking .
Max Schwarzer, Johan Obando-Ceron, Aaron Courville, Marc Bellemare, Pablo Samuel Castro*, Rishabh Agarwal*
ICML 2023
With scaling compute and model size along with appropriate design choices, value-based methods achieve super-human performance in the Atari 100K, while being 4x compute efficient than SOTA.
Aviral Kumar, Rishabh Agarwal, Xinyang Geng, George Tucker, Sergey Levine
ICLR 2023 (Top 5%), NeurIPS 2022 DRL Workshop Best paper Runner-up
With appropriate design choices, offline Q-learning exhibit strong performance that scales with model capacity. The secret ingredients were training on a large and diverse offline dataset with ResNets, distributional C51 backups and feature normalization (that is make RL training look more like SL).
Rishabh Agarwal, Max Schwarzer, Pablo Samuel Castro, Aaron Courville, Marc G. Bellemare
NeurIPS 2022
This work proposes an alternative research workflow to tabula rasa RL, where prior computational work (e.g., learned policies) is transferred from agent to another.
Rishabh Agarwal, Max Schwarzer, Pablo Samuel Castro, Aaron Courville, Marc G. Bellemare
NeurIPS 2021 (Outstanding Paper Award)
Our findings call for a change in how we evaluate performance on deep RL benchmarks, for which we present more reliable protocols and an open-source library , easily applicable with *even a handful of runs*, to prevent unreliable results from stagnating the field.
Rishabh Agarwal, Marlos C. Machado, Pablo Samuel Castro, Marc G. Bellemare
ICLR 2021 (Spotlight)
To improve generalization, we learn representations, via a contrastive loss, that puts states together with similar long-term optimal behavior. This is orthogonal to existing approaches such as data augmentation. An earlier version was accepted as an oral presentation at NeurIPS 2020 Workshop on Biological and Artificial RL.
Aviral Kumar*, Rishabh Agarwal*, Dibya Ghosh, Sergey Levine
ICLR 2021
We identify an implicit under-parameterization phenomenon in value-based deep RL methods that use bootstrapping: when value functions, approximated using deep neural networks, are trained with gradient descent using iterated regression onto target values generated by previous instances of the value network, more gradient updates decrease the expressivity of the current value network.
Caglar Gulcehre, Ziyu Wang, Alexander Novikov, Tom Le Paine, Sergio Gómez Colmenarejo, Konrad Zolna, Rishabh Agarwal,
Josh Merel, Daniel Mankowitz, Cosmin Paduraru, Gabriel Dulac-Arnold, Jerry Li, Mohammad Norouzi, Matt Hoffman, Ofir Nachum,
George Tucker, Nicolas Heess, Nando de Freitas
NeurIPS 2020
We propose a benchmark called RL Unplugged to evaluate and compare offline RL methods on a diverse range of domains. We provide detailed evaluation protocols for each domain and provide an extensive analysis of existing methods using these protocols. We hope that our suite of benchmarks will increase the reproducibility in offline RL and make it possible to study challenging tasks with a limited computational budget, thus making RL research both more systematic and more accessible across the community.
Rishabh Agarwal, Dale Schuurmans, Mohammad Norouzi
ICML 2020 (Talk)
This paper popularized offline RL and showed that standard off-policy algorithms perform quite well in the fully off-policy / offline deep RL setting with large and diverse datasets. A previous version was titled "Striving for Simplicity in Off-Policy Deep Reinforcement Learning" and presented as a contributed talk at NeurIPS 2019 DRL workshop.